Given a 2D grid of size m x n and an integer k. You need to shift the grid k times.
In one shift operation:
Example 1: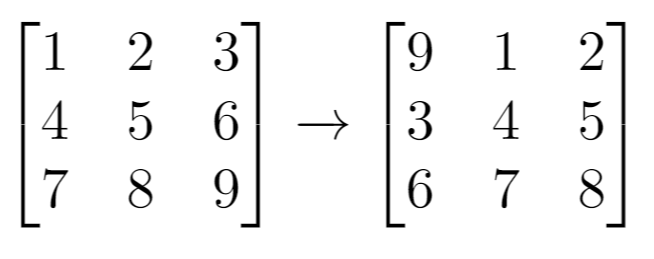
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 1
Output: [[9,1,2],[3,4,5],[6,7,8]]
Example 2: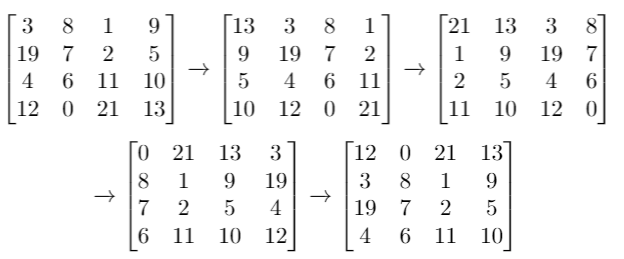
Input: grid = [[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10],[12,0,21,13]], k = 4
Output: [[12,0,21,13],[3,8,1,9],[19,7,2,5],[4,6,11,10]]
Example 3:
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]], k = 9
Output: [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Constraints:
* m == grid.length
* n == grid[i].length
* 1 <= m <= 50
* 1 <= n <= 50
* -1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 1000
* 0 <= k <= 100
此題給予一個m * n的矩陣及一正整數k,要求陣列元素在移動k步之後形成的陣列。
解法一:可以先使用雙向佇列存進陣列的所有元素,在使用Python的rotate函式移動陣列元素,最後將原陣列的元素更新成佇列裡的元素即可達成題目所求,不過此方法需額外建立雙向陣列提高了空間複雜度。
解法二:可以把元素移動k步這個步驟視為將後面k個元素挪到陣列前面,進而重組陣列,此方法的空間複雜度為O(1)。
from collections import deque
class Solution:
def shiftGrid(self, grid: List[List[int]], k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
# Minimum movement needed
move = k % (len(grid) * len(grid[0]))
if move == 0:
return grid
res = deque()
for i in grid:
for j in i:
res.append(j)
res.rotate(move)
col = len(grid[0])
for i in range(len(res)):
grid[i//col][i % col] = res[i]
return grid
class Solution:
def shiftGrid(self, grid: List[List[int]], k: int) -> List[List[int]]:
col, nums = len(grid[0]), sum(grid, [])
k = k % len(nums)
nums = nums[-k:] + nums[:-k]
return [nums[i:i+col] for i in range(0, len(nums), col)]
希望透過記錄解題的過程,可以對於資料結構及演算法等有更深一層的想法。
如有需訂正的地方歡迎告知,若有更好的解法也歡迎留言,謝謝。
